NASA
A newly discovered “super-Earth” raises hope for life in our immediate galactic neighborhood.
no time? Blue News sums it up for you
- A newly discovered exoplanet meets all the theoretical conditions to harbor life.
- TOI-715 b is located in our neighborhood and is classified as a “superland”.
- Only future studies can show the true conditions on the planet.
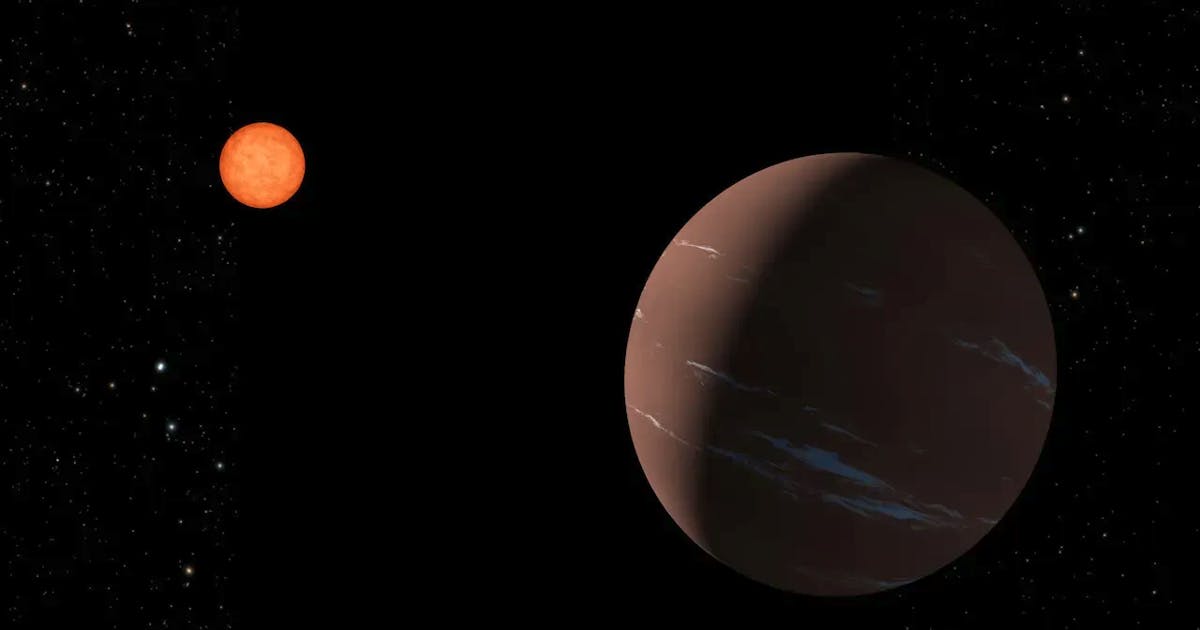
Astronomers have a “super-Earth” in our area Discover. The planet with the memorable name TOI-715 b is located about 137 light-years away – a stone's throw by cosmic standards.
“Super-Earths” are solid-surface planets that are heavier than Earth but lighter than Uranus. TOI-715 b is also located in its star's habitable zone, meaning it is just the right distance from it for liquid water to exist on its surface.
The planet orbits a small star
It is still not entirely clear whether there is actually water or even life on the planet TOI-715 b. The planet was discovered using the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). It orbits a red dwarf whose mass is less than one-tenth the mass of the Sun.
Most potentially habitable exoplanets discovered so far orbit red dwarfs. However, this does not mean that this class of stars is particularly destined for life, but it is a result of current technical limitations in astronomy.
The transit method favors the detection of red dwarfs
In the case of red dwarfs, the habitable zone is much closer to the star than is the case with the Sun, for example, because red dwarfs emit less heat. For example, the planet TOI-715 b orbits its star once every 19 days.
Exoplanets are discovered largely using the transit method, in which an exoplanet moves in front of its star as seen from Earth and temporarily reduces its brightness. Of course, if this happened every few weeks instead of just once a year, the chance of detection would be much higher.
Once an exoplanet is found, it can be analyzed in more detail, especially by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). It can determine whether a planet has an atmosphere in several ways, and if so, what molecules it is composed of.
The star could pose a danger to its planets
However, it is not yet certain whether red dwarfs actually provide the good basic conditions for life. One of the biggest concerns is that recurring solar flares from red dwarfs regularly destroy the atmospheres of their very nearby planets, preventing life from establishing.
However, TOI-715 b is considered a promising candidate by Nose. There may also be another planet in the same star system that could have roughly the same mass as Earth. However, its existence has not yet been definitively confirmed.

“Prone to fits of apathy. Zombie ninja. Entrepreneur. Organizer. Evil travel aficionado. Coffee practitioner. Beer lover.”






More Stories
Do you already know Ruona? -Dukchik
The “Dragon” must move to the International Space Station
Mysterious methane on Mars: NASA has a new theory