Climate change: The big collapse
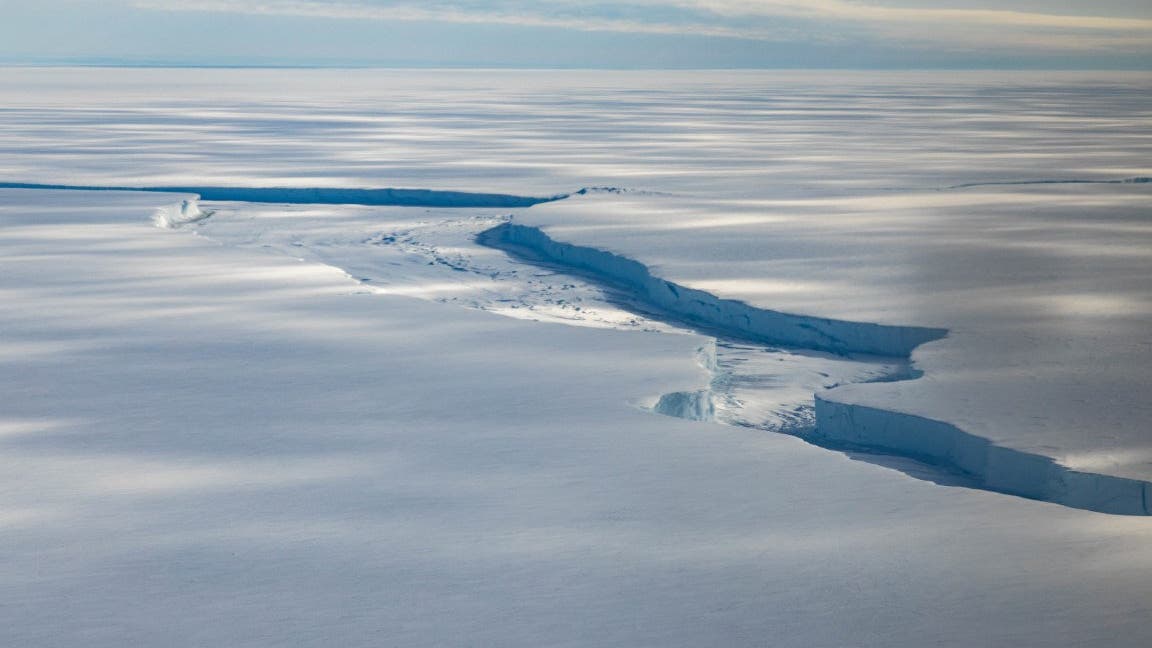
In just 25 years, 40% of Antarctic ice shelves have lost significant volume. West Antarctica is particularly severely affected.
© Sebastian Gleich / British Antarctic Survey / Cover images / Image Alliance (detail)
A gap opens in the ice shelf: this is now often the beginning of the end for ice fields. It disintegrates and dissolves in the sea. (archive photo)
2023 has not been a good year for Antarctic sea ice: even in the middle of the Southern Hemisphere winter, large parts of the Southern Ocean have not frozen over; Overall, average ice cover was well below the long-term average. In addition to the relatively thin sea ice, the thick bands of ice shelves on the edges of Antarctica are also in worse shape. 40% of these areas lost much of their area between 1997 and 2021. As an analysis by Benjamin Davison of the University of Leeds and his team shows in Science Advances..
According to the working group’s data, 71 of the 162 ice shelf areas were affected by the loss, resulting in a total of 7.5 trillion tons of ice disappearing and ending up in the sea as meltwater. The loss occurred almost exclusively on the western side of Antarctica, while the ice shelf on the eastern side increased in some cases. The export of 67 trillion tons of ice to the oceans offset the intake of 59 trillion tons of ice, resulting in an overall negative balance.
This is closely related to the oceanic conditions around the continent. “The western side is exposed to relatively warm conditions, while the eastern part is protected from the coast by a strip of cold water,” says Benjamin Davison. Ocean currents and prevailing winds push warm water beneath the West Antarctica ice shelf, attacking the pack from below and melting it. In extreme cases, the ice shelf also collapses, as has happened several times in recent years.
“We assumed that most Antarctic ice shelves go through cycles of rapid but short-lived shrinkage and then slow growth again. “Instead, we are now seeing nearly half of that amount shrink while there is no sign of recovery,” said Davison, who blames global warming.
© Benjamin Davison, University of Leeds (details)
Water temperatures around Antarctica | The water area in western Antarctica is as large as 2 degrees Celsius, which is enough to melt the ice shelf. In the east, the sea is colder.
Ice shelves form powerful masses of ice that float on the sea around Antarctica: they essentially form the ocean-side end of the Antarctic ice sheets and act as a barrier that slows or prevents the flow of inland glaciers. As ice shelves thin or shrink, these seals become weaker. Glaciers can flow out to sea more quickly and break up there, contributing significantly (unlike melting ice shelves) to sea level rise.
The working group observed some of the largest losses at the Getz Ice Shelf, where 1.9 trillion tons of ice was lost over the 25-year study period. Only five percent of this can be attributed to the calving process, where large chunks of ice break off the shelf and fall into the sea. The rest was to dissolve in the base. The Pine Island ice shelf has decreased by 1.3 trillion tons of ice. Here childbirth contributed at least a third. In contrast, the Amiri Ice Shelf, located on the eastern side of Antarctica, gained 1.2 trillion tons of ice. It is surrounded by significantly cooler water.
The water that enters the ocean from ice shelves and glaciers is fresh water. Researchers estimate that at least 67 trillion tons of freshwater entered the Southern Ocean between 1997 and 2021, which could have consequences for circulation: In the Southern Ocean, dense salt water sinks into the deep sea as part of global ocean currents, which is one of the This conveyor belt drives. Desalination makes seawater lighter and less salty, which means it takes longer to sink. In the long run, this will likely weaken the engine and thus transport cold deep water. The first signs of this have already begun to appear, as one study has shown.
Please allow Javascript to maintain the full functionality of Spektrum.de.

“Alcohol buff. Troublemaker. Introvert. Student. Social media lover. Web ninja. Bacon fan. Reader.”






More Stories
How is it treated and how can it be prevented?
Research has found that the T. Rex dinosaur was as intelligent as a giant crocodile
Hypoallergenic sunscreens for allergy sufferers